The carbon credit market is booming, fueled by an increasing number of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) regulations and initiatives. And some numbers do attract the investor’s eye. Not only has the number of credits purchased in 2020 doubled compared to 2017, but the demand for them is expected to increase exponentially. The best part for investors? Credits will also cost more, reaching $80-150 per tonne by 2035. All this is contributing to the growth of the voluntary carbon market, which is expected to be worth $100 billion/year by 2050.
Naturally, companies want to tap into this fast-developing sector. There are many options for investment in solutions that make carbon credit trading easier and more reliable. This is where blockchain technology steps in. For some time now, Unicsoft has been exploring how blockchain can be used to power carbon credit platforms, so we’re ready to share insights with you.
This article will explain how the voluntary carbon market works, why you should consider investing in it, and how blockchain helps create reliable trading solutions. Plus, we’ll give some examples of successful blockchain carbon credit products, including one developed by Unicsoft.
Let’s get started!
How the voluntary carbon market works
The carbon emission credit system works on a cap-and-trade basis. A state regulator assigns a carbon emission quota (in credits) based on a company’s activity and size. If a company emits less CO2 than its assigned quota, it can sell or trade its remaining credits with other companies. If it produces more, it must buy extra credits. Very often, credits are sold by companies that have surplus carbon credits or that are seeking other options on the voluntary carbon market to comply with regulations and avoid fines and extra taxes.
The voluntary carbon market deals with credits generated by carbon reduction initiatives. These are usually projects related to renewable energy, energy efficiency improvement, GHG capture and sequestration, land use, and reforestation.
Now that we’ve looked at how the carbon credit market operates let’s turn to the most important question.
Why invest in the carbon credit market?
There are two ways to tap into the investment opportunities presented by this dynamic market:
- Invest directly in carbon credits as assets.
- Invest in developing blockchain carbon credit solutions to meet the demands of voluntary carbon credit markets.

There are a few solid reasons why the second option may be a smarter move.
- High growth potential. With the rise of global temperatures, organizations worldwide are seeking new ways for technology to accelerate the transition to clean energy and combat climate change. Much of what we perceive as initiative today will become an obligation tomorrow.
- A growing trading base. As the carbon credit market expands, more corporate and individual clients will be willing to create, purchase, or trade their carbon credits. They will need secure digital solutions for this.
- Heightened investor interest. Developing more technologies for carbon credits will speed up the broader adoption of voluntary carbon credit markets, attracting even more investors.
- A green investment in itself. Developing a carbon trading platform can be a part of your long-term sustainability initiatives. Plus, you can invite partners to participate in programs, buy credits, and help reach net zero faster.
Suppose you’re thinking of creating a digital product within the carbon credit market. In that case, you need to harness the right technologies to ensure safe data processing and transactions, proper verification, and fast auditing. And blockchain is a perfect choice.
Why are blockchain carbon credits projects gaining traction?
As CO2 reduction policies and initiatives have multiplied, so have carbon markets, credits, and other trading mechanisms. The problem is these trading mechanisms are disparate across countries and regions. This has created critical problems in the carbon credit market, such as:
Furthermore, high transaction costs and commissions mean that current carbon trading market solutions mostly enrich brokers and operating agents.
All these factors only add to the complexity of market operations and do little to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. So how can you change the situation by building a blockchain carbon credit solution?
The blockchain is a safe, reliable, efficient, open, and inclusive platform. This makes it suitable in many ways for implementing carbon credit market initiatives.
- A distributed blockchain ledger can ensure transparent issuing and tracking of carbon credits, eliminating over-crediting and double-counting.
- Blockchains are more accessible to small and medium-sized businesses as they reduce the entry threshold for the carbon trading market.
- Blockchain ensures that the information companies provide is immutable, transparent, and easily accessible.
- Reliability and accessibility of information can streamline communication between market participants.
- Ultimately, a blockchain can reduce transaction costs and control the flow of money and data within these markets and their participants.
Let’s look at how these blockchain benefits translate into market solutions you can invest in.
Blockchain-based carbon credit solutions
The carbon credit environment brings together the organizations that create, issue, regulate, or trade voluntary carbon credits. Usually, this all happens on a digital platform, and blockchain can be used in the processes and services the platform provides.
Let’s review the main types of solutions available.

Carbon offset tokenization
Digital tokens — whether fungible (like cryptocurrency), semi-fungible (like tickets or vouchers), or non-fungible (NFTs of all sorts) — make it easy to access and trade carbon credits on the blockchain. The process of converting carbon credits into investable assets (tokens) is called tokenization. Tokenization is handy when a company with a carbon credit surplus wants to sell or trade its credits.
One token equals one carbon credit, which gives the owner the right to emit or compensate for one tonne of CO2. A token includes information about the credit, such as the issuing organization, credit certification, auditing data, transaction logs, and project information. Blockchain saves this information in distributed ledgers, allowing for more traceability and data standardization.
This data provides the basis for a smart contract: a program that begins to operate if specified criteria are met. A third-party company can verify a token’s data and check its ownership. Once these are confirmed, the contract executes automatically without any intermediary involved, and the tradable token is created. After a company has created a certain number of tokens, it can sell them on a crypto exchange platform.
Worldwide carbon credit project registries
Open-source and public blockchains are now seen as a way to bring higher integrity to environmental projects. The avalanche of climate mitigation projects, including carbon credit-related ones, hasn’t had an immediate positive effect on the environment. Many projects at the local, regional, and global levels suffer from a lack of transparency and questionable efficiency.
While offset generation data is publicly available, there’s no unified database that aggregates this information. This makes it difficult to determine how many carbon projects are active and how much CO2 they have already helped offset.
Blockchain technology adds transparency and clarity to relationships between carbon market participants worldwide. As a permanent, publicly-held record that nobody owns or can edit but anybody can view, blockchain brings better visibility and digitization to carbon credit systems. Ultimately, this should force less efficient projects to drop out and give support to genuine, market-attractive initiatives.
The World Bank’s International Finance Corporation (IFC) division took a step in this direction and launched a blockchain-based project to register carbon removal initiatives. The project aims to keep crypto investor interest but steer investors toward verified and efficient carbon credit projects.
Carbon credit platforms
Blockchain carbon credits platforms are the most popular application of technology to carbon credits. These platforms allow users to create, store, tokenize, sell, and (sometimes) exchange carbon credits. To do this, they give users access to the following:
- Carbon credit tokenization
- Smart contract creation
- Secondary markets
Some platforms, such as AirCarbon Exchange, offer credits from around the globe but tokenize them on their own platform. Others, like Toucan, provide ready-to-use tokens that can be sold on major crypto exchanges like Binance and Coinbase.
Carbon credit platforms also allow companies to mint NFTs that represent carbon credits. Companies can mint carbon credit NFTs on the platform and sell them on decentralized NFT marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible.
Popular blockchain carbon credits platforms
ESG and climate tech companies offer numerous blockchain-based carbon credit platforms for corporate and individual clients. Here are some of the better-known ones.
KlimaDAO
KlimaDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization with a platform offering carbon credit minting, tokenization, and trading to both organizations and individuals. The organization has its own KLIMA tokens that are minted and distributed automatically.
One of the most distinctive features of KlimaDAO is that its tokens are backed by BCT (Base Carbon Tonne) tokens created by Toucan. BCT is linked to real assets, which helps KlimaDAO push the carbon-based ecosystem forward, drive carbon credit prices higher, and get more market exposure.
Moss NFT
Moss Amazon NFT is a project that takes the carbon credit industry into Web3. The project has minted NFT-based tokens stating the number of acres of the Amazon forests that the NFT owner is obliged to preserve. The NFT is a digital certificate that proves the owner’s rights to property and protection of the actual land. Moss NFT owners can monitor their part of the Amazon preservation project and organize visits to see it.
Toucan
Toucan provides infrastructure for Web3 builders, credit suppliers, and credit buyers. It features two types of credits: BCT (Base Carbon Tonne) and NCT (Nature Carbon Tonne).
These credits are tokenized as a unified reference token called TCO2. TCO2 tokens are stored on a smart contract on the Open Climate Registry, a blockchain database. This unification helps the platform issue tokens that can be traded within Toucan’s ecosystem and on major crypto exchanges. Plus, it makes the registry information transparent, which improves market adoption.
Carbon credit platform development at Unicsoft: A case study
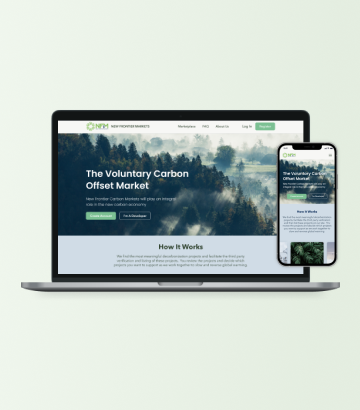
New Frontier Markets (NFM) is an energy technology that develops blockchain and web-based applications for the carbon and commodity markets.
NFM asked Unicsoft to develop a digital marketplace for corporate and individual investors to acquire and trade carbon credits. These credits are issued on the platform as NFTs, which owners can trade after purchase. The NFTs represent verified carbon credits and are minted on a private blockchain which can only be accessed through the platform.
Unicsoft developed an MVP of a platform with the following features:
- A blockchain-native currency for credit trading
- Special consensus protocols to ensure security and data privacy
- Compatibility with major mobile and desktop web browsers
- Guaranteed 24/7 uptime for all platform modules
- Support for monetization of primary and institutional sales
- Easy transfer of NFTs to crypto wallets
The full-scale product, named Frontier Carbon Solutions, features two components — retail and institutional platforms — to meet the needs of the user roles the Unicsoft team identified for the project. The roles are
- Project developers. These users are companies offering the service of collecting and safely storing the CO2 they capture in some kind of facility. The platform verifies the users and checks all the documents certifying the amount of CO2 they plan to trade on the platform.
- Basic customers. Basic customers use the retail platform to buy carbon credits that compensate for the amount by which they exceed the allowable limit.
- Advanced customers. This category of users can purchase carbon credits for offsetting (similar to basic customers) and also resell credits they have purchased from project developers.
The unified platform provides capital-raising opportunities for project owners and helps investors choose which carbon offset projects to support. All business features benefit from the transparency, efficiency, and reliability of blockchain technology. You can read the full case study here.
Factors to consider when launching blockchain carbon credit projects
Linking blockchain technology to a carbon credit solution allowed our experts to understand the opportunities for blockchain technology in this niche. The Unicsoft team also encountered the main risks and challenges associated with such projects. Based on our experience, here are some important aspects to consider when planning a blockchain-based carbon credit platform.
Choosing a blockchain platform and consensus mechanisms
It’s no secret that blockchain technology is energy-intensive. The energy required to create crypto assets and trade tokens often creates a footprint that defeats the aim of carbon emission reduction. As a result, you need to choose solutions that require fewer system resources.
That’s exactly what we did for the Frontier Carbon project. During the discovery phase, we established that building on the Cosmos blockchain leads to more predictable resource usage, while implementing the Tendermint consensus protocol takes fewer resources than other proof-of-work algorithms.
Payment processing
You have to carefully consider how your platform will receive and process payments — not just technically but also in terms of tax and legal implications. Consider consulting with a team of seasoned business analysts and solution architects to handle this issue.
Trading engine
The trading engine lies at the heart of your carbon credit project and is responsible for the core functionality of your platform. Among other things, it controls user accounts, creates charts reflecting price dynamics, matches offers and rates, and processes real-time prices and commissions. It also specifies order books and trading lists that document a credit’s trading activity on the platform.
There are two main trading engine options: using a ready-to-go marketplace or exchange solution or going for a proprietary solution.
For our project, we began with an engine from a custom crypto exchange. However, as work developed, we realized that only a proprietary engine would meet the business logic requirements for the platform.
Value and supply chain management
Voluntary carbon markets that rely mostly on brokers and traders to match project developers’ supply and end users’ demand often need more transparency and integrity in their supply chains.
Blockchain, in this case, becomes the right choice. First, to have a clear vision of the companies emitting carbon and companies sucking carbon from the atmosphere as well as the amounts they operate with. Second, blockchain technology ensures that all the relations and transactions between supply chain participants happen not on a private conversation or who knows how else but through a write-only ledger that records and stores all the transactions.
This way, a blockchain-based carbon credit platform will help you achieve end-to-end traceability, security, and coordination that voluntary carbon credit markets really lack.
Wrapping up
The rapid growth of carbon credit markets has created opportunities for investors in online trading technology. Alongside carbon credit asset and tokenization tools, blockchain carbon credits platforms are an attractive investment option. Platforms speed up the adoption of carbon credits, promote carbon market transparency, and help organizations launch more ESG projects.
However, both blockchain and carbon credit trading are complex. For the best chances of success and to avoid the many pitfalls, it makes sense to delegate platform development to a tech vendor with experience in creating robust, secure, and scalable solutions.
Unicsoft, a blockchain development company, is ready to talk about your project and advise on how to make it work. Contact us, and let’s discuss how your company can take part in the carbon credit market and enjoy a healthy ROI!





![Blockchain and Carbon Credits: Why Invest? What’s the EU Artificial Intelligence Act and How to Comply? [Webinar]](https://unicsoft.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Cover_1140_v1.1-370x280.png)

